This definitive guide seeks to unravel the intricacies of e-commerce development, providing an in-depth exploration of its essence, mechanics, and indispensable role in the success of contemporary enterprises and dive into building an ecommerce website from scratch.
Reading time: 18 min.
E-commerce development is a transformative force, reshaping how businesses connect with their audience. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the digital storefront has emerged as a vital conduit for enterprises to survive and thrive in the global marketplace.
As businesses worldwide navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape, a nuanced understanding of e-commerce development becomes an advantage and a necessity for those aspiring to carve their niche and thrive online.
E-commerce development is more than just a technological evolution; it is a comprehensive strategy encompassing online platform creation, design, and continuous enhancement, allowing businesses to showcase and sell their products or services to a diverse and expansive audience. This definitive guide seeks to unravel the intricacies of e-commerce development, providing an in-depth exploration of its essence, mechanics, and indispensable role in the success of contemporary enterprises and answers the question how to create a website for e-commerce.
E-commerce website development refers to creating, designing, and maintaining online platforms where businesses can conduct electronic transactions, primarily selling products or services to customers online. This specialized form of website development involves a combination of technology, user interface design, and business strategy to create a seamless and secure online shopping experience.
Ecommerce website development can be achieved through various platforms and technologies, such as Shopify, Magento, WooCommerce (built on WordPress), and custom-built solutions. The choice of platform often depends on factors like business requirements, budget, and the desired level of customization. Effective Ecommerce development involves the technical implementation of these features. It focuses on creating a user-friendly interface, optimizing performance, and ensuring the security and reliability of the online shopping experience.
Here are some of the critical types of Ecommerce business models. Each of these business models has unique characteristics and implications for Ecommerce development. The choice of a particular model depends on the nature of the products or services, the target audience, and the overall business strategy. As the Ecommerce landscape continues to evolve, businesses may also explore hybrid models or innovative approaches to cater to changing consumer behaviors and market dynamics.
In B2B ecommerce website development, transactions occur between businesses. It can involve the sale of products, services, or both.
B2C Ecommerce involves businesses selling products or services directly to individual consumers.
This model involves businesses selling products or services to other companies, which, in turn, sell to end consumers.
In B2G Ecommerce, businesses sell products or services to government agencies.
In this model, individual consumers offer products or services to businesses.
D2C ecommerce website development involves brands or manufacturers selling their products directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels.
C2C Ecommerce facilitates transactions between individual consumers.
Ecommerce site development offers numerous advantages, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. Let’s look at the ecommerce advantages and disadvantages:
While e-commerce online store development offers immense business opportunities, it is essential to address the associated challenges proactively to ensure sustained success in the competitive online landscape.
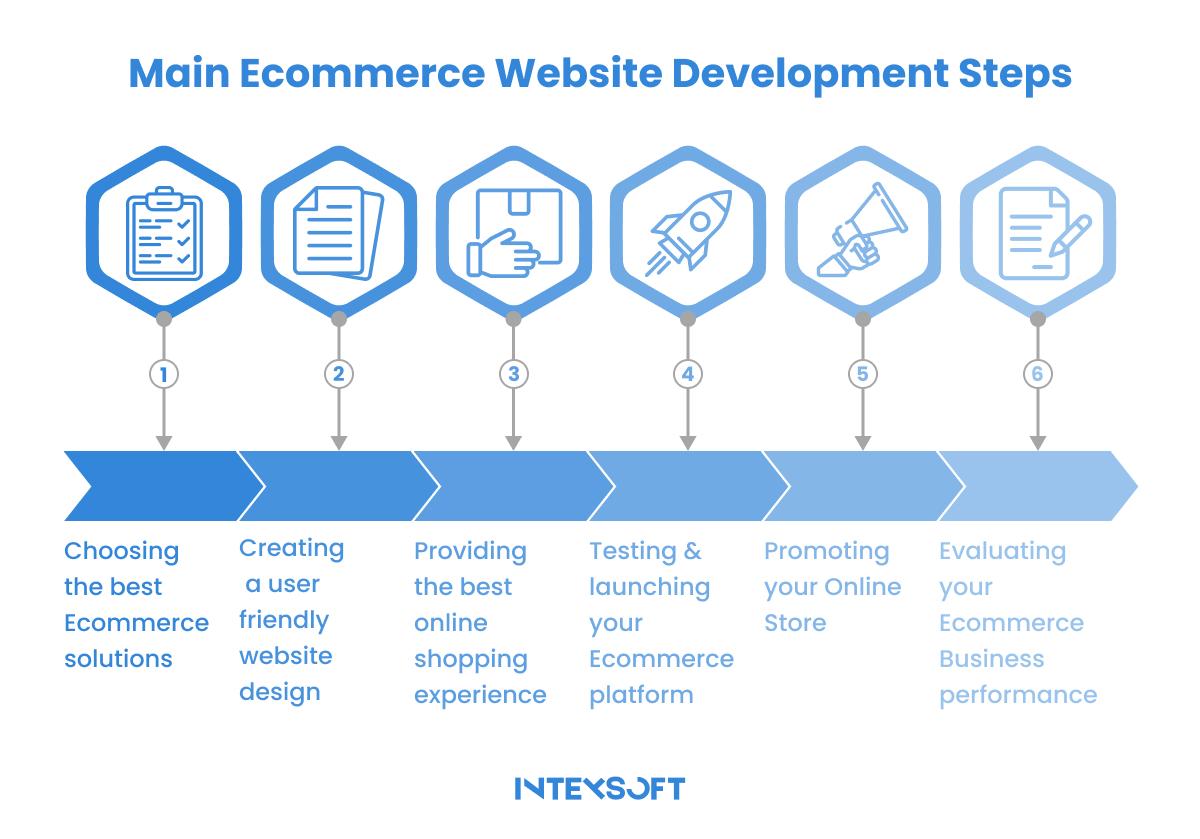
By following these steps in the Ecommerce web development process, you can create a user-friendly, secure, and prosperous online platform that meets your audience’s needs and contributes to your business’s growth.
Before diving into e-commerce website building, one of the crucial things to consider when building an ecommerce website is to have a deep understanding of your target audience. Research their preferences, behaviors, and expectations. This knowledge will inform critical decisions throughout development, ensuring your Ecommerce site resonates with your audience.
Selecting the appropriate Ecommerce platform is a pivotal decision. Consider factors such as scalability, customization options, security features, and ease of use. Popular platforms include Shopify, Magento, WooCommerce, and custom-built solutions. The platform you choose should align with your business goals and cater to the needs of your audience. Also, if your business requires a lot of flexibility, consider developing your custom platform to be tailored to the individual characteristics of your business.
A skilled and experienced development team is instrumental in the success of your Ecommerce project. Look for professionals with expertise in Ecommerce development, including web designers, developers, and possibly specialists in SEO and security. Depending on the technology stack and platforms you choose for development, such as PHP, Magento, Drupal, etc., you may need a specific specialist. A collaborative and communicative team will help streamline the development process and ensure a high-quality end product.
Your e-commerce site’s visual appeal and user experience are paramount. Work on creating an intuitive and visually appealing layout that aligns with your brand identity. Pay attention to navigation, product displays, and a seamless checkout process. Responsive design is essential to ensure a consistent experience across various devices.
Integrate essential features and functionalities into your Ecommerce site. It may include a secure payment gateway, inventory management system, customer relationship management (CRM) tools, and analytics. Consider the needs of your audience and business goals when choosing integrations to enhance the overall user experience.
Develop a robust content strategy to engage and inform your audience. It involves creating compelling product descriptions, high-quality images, and multimedia content. Implement SEO best practices to enhance visibility in search engines and drive organic traffic. A well-executed content strategy contributes to a more immersive and informative Ecommerce experience.
Thorough testing is essential to identify and rectify any issues before launching your Ecommerce site. Conduct usability testing, check for responsive design across devices, and ensure all functionalities work seamlessly. Test payment processes, form submissions, and any integrated third-party tools. Address any bugs or issues to guarantee a smooth and error-free user experience.
After successful testing, launch your Ecommerce site. Monitor its performance closely and gather user feedback. Continuous improvement is critical to staying competitive and meeting evolving customer expectations. Regularly update content, analyze user behavior, and implement improvements based on real-time data.
The cost of e-commerce development can vary significantly based on various factors, including the complexity of the project, ecommerce website development packages, features and functionalities required, the choice of platform, the development approach, and the development team’s location and expertise. For example, we have researched the Magento website cost and how to build marketplace on various platforms in detail. Now, let’s look at the key factors that influence the cost of Ecommerce development:
The choice of an e-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify, Magento, WooCommerce, custom-built solution) can significantly impact costs. Some platforms are subscription-based, while others may involve one-time licensing fees.
The complexity of the website design and the customization level required will affect costs. Custom designs, graphics, and branding elements may increase development expenses.
The number and complexity of features integrated into the Ecommerce site, such as payment gateways, inventory management, user authentication, and third-party integrations, will impact costs.
The expertise and location of the development team influence costs. Development rates vary globally, with teams in regions with higher living costs generally charging more. Additionally, hiring experienced professionals may come at a premium.
The hosting infrastructure, server requirements, and associated maintenance costs contribute to the overall expense. Robust hosting solutions with security features may involve higher ongoing costs.
Costs related to content creation, including product descriptions, images, and multimedia content, can vary based on the scale and quality of the content needed.
Thorough testing is essential for identifying and fixing bugs. Quality assurance processes, including usability, security, and performance testing, can add to the overall cost.
Ongoing maintenance and support services must address updates, security patches, and potential issues post-launch. Budgeting for continuous improvements and support is crucial.
Incorporating marketing and SEO strategies into the development process may increase costs. These strategies include optimizing the site for search engines, implementing digital marketing campaigns, and integrating analytics tools.
Designing the website with scalability in mind can impact costs. Consideration for future growth and the ability to handle increased traffic and functionality additions may influence the initial investment.
It’s important to note that e-commerce development costs can range from a few thousand dollars for a small, essential website to hundreds of thousands for large, complex projects.
It is essential to consider that custom ecommerce website development will require more significant costs than creating a website on existing platforms.
Additionally, ongoing expenses such as hosting, maintenance, and marketing should be factored into the overall budget for a comprehensive understanding of the total cost of Ecommerce development.
By incorporating best practices into your E-Commerce development process, you can create a robust, user-friendly, and secure online shopping platform that meets your customers’ needs and supports your business’s growth.
Throughout building a ecommerce website it is essential to ensure your site is optimized for mobile devices. Many users shop on smartphones, so a mobile-friendly design is crucial for a positive user experience.
Prioritize a user-friendly design with intuitive navigation, precise product categorization, and easy checkout processes. Focus on providing a seamless and enjoyable shopping experience.
Optimize your site for quick loading times. Slow websites can lead to high bounce rates. Compress images, minimize HTTP requests, and leverage browser caching to improve loading speed.
Implement secure and trusted payment gateways to protect customer data during transactions. Use HTTPS and comply with industry standards to ensure a secure online shopping environment.
Connective eCommerce is an advanced approach to managing ecommerce store operations. Unlike traditional methods that rely on separate software applications, Connective eCommerce emphasizes the seamless integration of various components within an eCommerce ecosystem.
Simplify the checkout process to reduce cart abandonment rates. Minimize the number of steps, offer guest checkout options, and provide a progress indicator to keep users informed.
Integrate social media into your Ecommerce site to enable easy sharing of products and user-generated content. Leverage social platforms for marketing and customer engagement.
Implement search engine optimization (SEO) best practices to improve your website’s visibility in search engine results. Optimize product pages, meta tags, and images to enhance organic search traffic.
Offer responsive and accessible customer support. Provide multiple channels for customer inquiries and ensure timely and helpful responses. A positive service experience contributes to audience satisfaction and loyalty.
Custom ecommerce Development refers to creating a tailored online shopping platform that specifically meets a business’s unique needs and requirements. Unlike using pre-built Ecommerce platforms, custom Ecommerce development involves building a solution from the ground up, offering a high degree of flexibility and customization.
Custom soft development can require the expertise of WordPress developers, Magento developers, and Shopify developers. These specialists’ expertise in working with e-commerce platforms can play a crucial role in tailoring online shopping platforms to meet businesses’ unique needs.
Before embarking on the ecommerce website design and development process, businesses should carefully outline their requirements, prioritize features, and work with experienced professionals to obtain accurate cost estimates.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) compliance is crucial for e-commerce businesses that operate in the European Union (EU) or handle the personal data of EU residents. GDPR sets guidelines for the lawful and transparent processing of personal data, providing individuals greater control over their information. Let’s look at some vital considerations for GDPR compliance in e-commerce.
Understand and document the flow of personal data within your E-Commerce system. Identify the types of data collected, processed, and stored, along with the purposes for which they are used.
Clearly define the lawful basis for processing personal data. For Ecommerce, this often involves obtaining user consent for data processing, especially during checkout.
Provide clear and concise privacy notices informing users how their data will be processed. Include information about the purpose of data collection, the legal basis for processing, and details about third-party data sharing, if applicable.
Obtain explicit and informed consent from users before processing their data. It is essential for email marketing, user accounts, and storing payment information.
Collect only the necessary data required for the intended purpose. Avoid excessive data collection and review your data to ensure it remains relevant.
Uphold individuals’ rights, including the right to access, rectify, erase, or restrict the processing of their data. Implement procedures to handle such requests on time.
Implement robust security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction. Encryption, secure hosting, and regular security audits are essential.
Develop a data breach response plan to address any security incidents promptly. Report data breaches to the relevant supervisory authority within the specified timeframe and inform affected individuals when necessary.
If you use third-party processors (e.g., payment gateways, analytics tools), ensure they comply with GDPR standards. Review and update data processing agreements with vendors.
If your Ecommerce site targets or collects data from individuals under 16 (or a lower age limit as defined by member states), obtain parental consent before processing their data.
Implement cookie banners or pop-ups to inform users about the use of cookies on your website. Obtain user consent before placing non-essential cookies, and provide options for users to manage their cookie preferences.
If you transfer personal data outside the EU, ensure that the destination country provides adequate data protection. Alternatively, implement safeguards, such as Standard Contractual Clauses or Binding Corporate Rules.
Conduct DPIAs for high-risk processing activities that involve new technologies or pose potential risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Train your staff involved in data processing on GDPR principles and compliance requirements. This includes awareness of data protection policies and procedures and the importance of safeguarding personal information.
Maintain records of your data processing activities. This documentation is essential for demonstrating GDPR compliance and cooperating with supervisory authorities if required.
Ensuring GDPR compliance helps businesses avoid legal repercussions and builds trust with customers who value protecting their personal information. Regularly review and update your compliance measures in response to changes in regulations and your business operations. Consulting with legal experts or data protection officers can provide valuable guidance in achieving and maintaining GDPR compliance for your Ecommerce business.
As the e-commerce landscape continues to evolve, several trends are shaping the future of e-commerce development. Businesses need to adapt to these trends to stay competitive and meet the changing expectations of consumers. So, let’s delve into some notable future trends in Ecommerce development.
With the rise of voice-activated devices like smart speakers and virtual assistants, voice commerce is gaining prominence. Ecommerce platforms are integrating voice search and command functionalities to provide a seamless shopping experience for users.
AR and VR technologies are enhancing the online shopping experience by allowing users to visualize products in a virtual space. Customers can try products virtually before purchasing, leading to a more immersive and informed shopping experience.
AI and ML are being leveraged for personalized product recommendations, chatbots for customer support, predictive analytics for inventory management, and fraud detection. These technologies enhance user engagement and optimize various aspects of Ecommerce operations.
PWAs combine the best features of both websites and native mobile apps, providing a fast and reliable user experience. They work seamlessly across devices and enable offline functionality, improving accessibility and user engagement.
Headless e-commerce separates the front and back of an e-commerce platform, allowing more outstanding design and user interface flexibility. This approach enables businesses to deliver content and products across various channels, including websites, mobile apps, and IoT devices.
Subscription models are becoming increasingly popular, especially in beauty, food, and entertainment industries. Ecommerce businesses offer subscription services to provide a recurring revenue stream and enhance customer loyalty.
Consumers are becoming more conscious of environmental issues, and there is a growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. Ecommerce businesses are focusing on sustainable practices, from product sourcing to packaging, to meet the preferences of environmentally-conscious consumers.
The global nature of Ecommerce is leading to increased cross-border transactions. Businesses leverage technology to overcome logistical challenges, offer localized experiences, and cater to a worldwide customer base.
Social media platforms are evolving into Ecommerce hubs. Businesses are integrating social commerce features to enable direct shopping within social apps, making the buying process more seamless for users.
Blockchain is being explored for its potential to enhance transparency and security in Ecommerce transactions. It can address issues related to fraud prevention, supply chain traceability, and secure payment systems.
With the continued growth of mobile users, emphasizing a mobile-first approach in Ecommerce development is crucial. Ensuring that Ecommerce websites are optimized for mobile devices is essential for reaching a broader audience.
Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, are being integrated into Ecommerce platforms to enhance security and streamline checkout.
There is a growing emphasis on creating inclusive E-Commerce experiences and ensuring accessibility for individuals with disabilities. It includes implementing features like voice commands, screen readers, and easy navigation.
These trends collectively shape the future of Ecommerce development, indicating a shift towards more innovative, user-centric, and technologically advanced online shopping experiences. As businesses navigate this evolving landscape, staying informed about these trends and adopting relevant strategies will be essential to sustained success in the Ecommerce industry.
E-commerce development involves planning, design, development, testing, deployment, marketing and SEO, analytics and optimization, and maintenance.
E-commerce development focuses specifically on creating online platforms for buying and selling. It involves implementing features like product catalogs, shopping carts, and secure payment gateways.
Web development encompasses the broader creation and maintenance of websites or web applications. It includes various types of websites beyond e-commerce, covering front-end, back-end, and full-stack development, and is not limited to online transactions; it can consist of informational sites, portfolios, and other applications.
As businesses embark on or refine their E-commerce journey, adapting to emerging technologies, staying attuned to customer preferences, and ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR are critical. E-commerce development is not merely a one-time endeavor; it is an ongoing process of adaptation, optimization, and innovation to meet the ever-changing demands of the digital marketplace.
In essence, the future of E-commerce development lies in the hands of those who embrace agility, creativity, and a customer-centric mindset. By staying informed, leveraging cutting-edge technologies, and prioritizing the user experience, businesses can meet and exceed online consumers’ expectations, fostering sustainable growth and success in the digital era.