
The conversation around blockchain and databases has been going on for a long time, but not everyone understands what it is and how to work with it.
That’s why we have decided to explain everything in simple words and sort the key concepts out.
Let us imagine a database that has only one table. There is nothing in this table except for 5-6 fixed columns. And all we can do in such a database is to insert and to read. No more operations can be performed.
Now imagine that every participant in a big game called Bitcoin has a copy of this Database. The software is designed in such a way that all these Databases are synchronized with each other, and, if you insert some data into it, then after a certain time all people with a copy of this Database will get this data. Because of such a system, fraud becomes impossible.
But today we will talk not only about databases but also analyze what cryptocurrencies and exchanges are, take a look at Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Speaking in simple terms, blockchain is a chain of blocks interlocked with each other. Each block has a neighboring block on each side. This is a kind of round dance, where new blocks can be added, but no one can leave it.
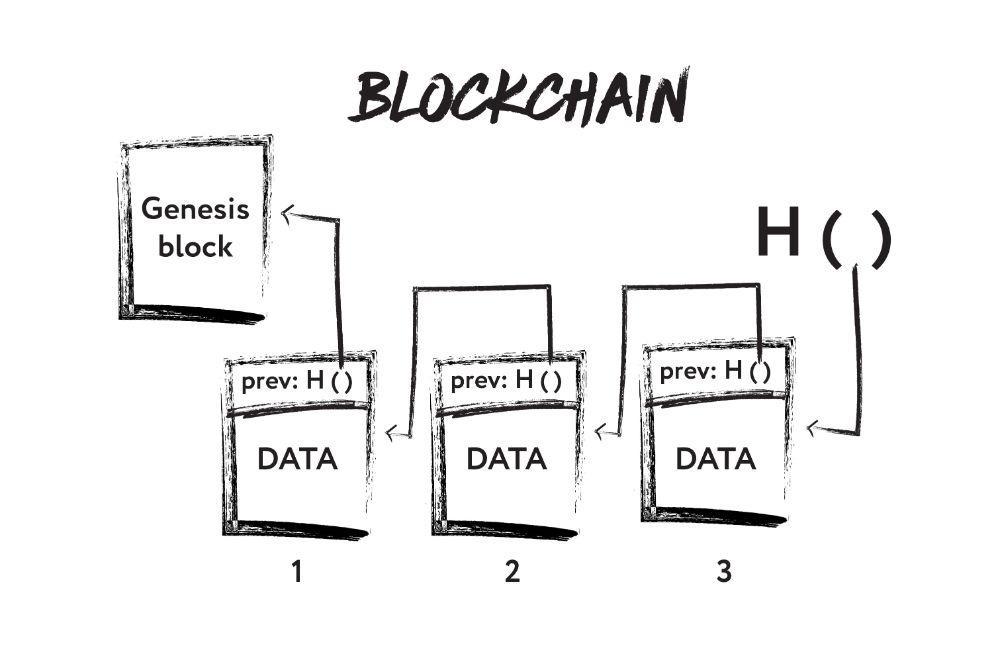
The blockchain has an initial block from which it all starts. It is the Genesis Block. As an analogy, we can give a simple list as an example in which always has a beginning or a root. As you go, a new block clings to the initial one and thus a chain begins to form. In order to connect the blocks, the H () function is used.
How can we link these blocks together and how is blockchain different from a regular list?
The matter is that there are mathematical Hash functions. They are SHA-1, SHA-2, etc. The peculiarity of these functions is that they allow you to transfer some data into them and get a string of characters (bits, as a rule) at the output. But such a function cannot work the other way around. It is simply impossible to get the source data from a string of characters.
Hash functions have an avalanche effect. Let’s say we have two sets of input data:
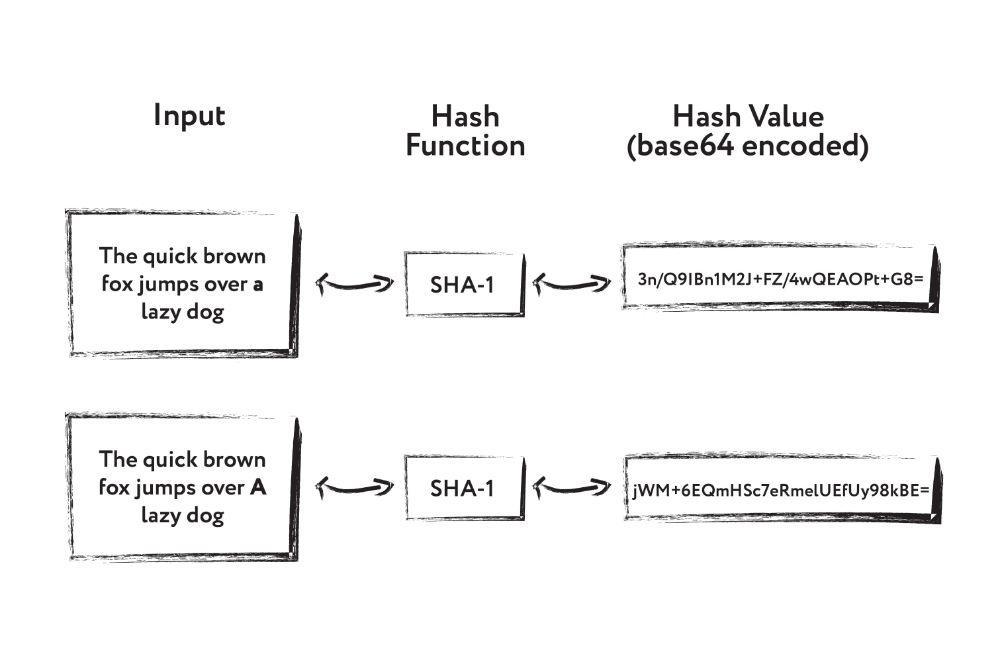
As we can see, there is one slight difference in the input data set. It is the capital letter A. When we examine the output value, we will see two completely different values. An avalanche effect of changing the Hash function occurs, not only the value of 1-2 bits is changed, but also of many others.
How can we use Hash functions to link all the blocks together?
Suppose we have a data block that contains some information. This can be the information of any nature such as a sentence, numbers, and structures. In addition, there is a field in each block, i.e. hash of the previous block. We have the initial block; it has nothing in this field because it has no previous block. To add a new block to the blockchain, you need to calculate the hash of the block to which we want to attach a new one. Having calculated hash, we enter it into a new block.

If we change any letter or data in the block, then the hash will change and the value will become different. In addition, when checking the chain, we will see that the values do not match. It will immediately become clear that hash was substituted or something is wrong with it. This is the whole consistency of blockchain data.
It is worth noting that Bitcoin is very fond of blockchain and is based on it. First, let us go a bit deeper into the history of blockchain creation and money evolution. How did it all start?
And all it started with a simple barter when people were exchanging things. But quite often, the exchange could not be done at an equal rate. For example, a cow was exchanged for 1kg of millet. Everything was complicated by the fact that there was no exchange unit.
Then came gold, which began to act as an exchange unit. But it was too little gold in the world and not everybody could afford it. This made trading and exchange difficult.
Therefore, new exchange units began to appear such as metal coins. Along with gold, bronze, silver and various alloys appeared. However, the problem of metal money is that it is very heavy.
Therefore, paper money started to appear. It is during this period that the turning point comes because, before that, money had a certain value in itself. And paper money is becoming fiat. Forget for a second that a paper bill any kind of a banknote. Then it becomes clear that it costs much less than what it really is.
From this moment begins the revolution in the history of money. The economy is going up, but fiat money is not secured by gold, but only by the state’s debt obligations. The state says that it undertakes to accept this money, and we can get something in return.
The amount of money grew, there became too much of it. Therefore, there was a need to store money somewhere, while keeping the ability to use it any time. So plastic cards appeared.
Following the plastic cards, electronic money appeared. Why do we need them? Many different currencies were used in the world and often, especially given the globalization of the market, it was necessary to find a way to conduct trading operations using some common currency. Electronic money was invented to find a way out of this situation.
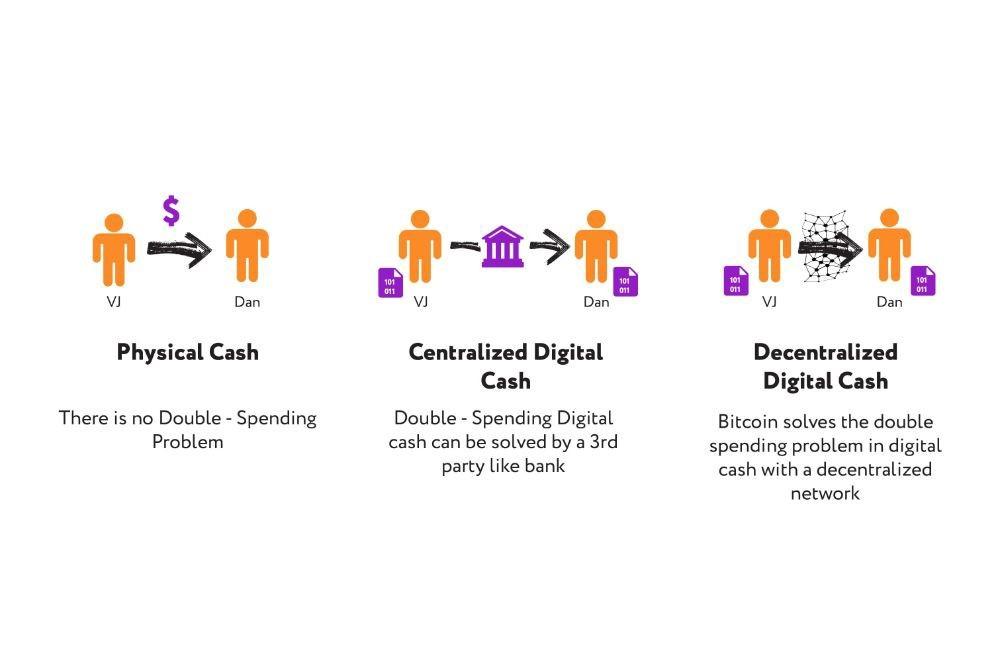
Then came cryptocurrency. But why cryptocurrency, if there is electronic money? Cryptocurrency solves one rather important problem, i.e. security. Protection of banknotes is provided with the help of watermarks. In the case of electronic money, the problem of double-spending is quite serious. If money is presented as some files in the database, then we can copy it. That is, it’s just a collection of bits that we can copy without problems, and it will not be possible to prove the data was copied and existed somewhere else.
But cryptocurrencies solve this problem with the help of blockchain. At the very beginning, we had physical money that could be transferred to another person, but the problem of double-spending did not arise. Then came electronic money. Here, in order to transfer this money from one person to another without any problems, the help of a third party is required. In this case, it may be banks that solve this problem of trust. Cryptocurrencies remove this intermediary through the blockchain. They provide a decentralized way to solve this problem.
The cryptocurrency blockchain is a distributed database. This means that there is no centralized authority on which everything depends; in this case, it is a bank. If something happens to the bank database, then people will lose all their money.
Here, a blockchain with a distributed database has a great advantage. This is the type of data that we can copy to many computers and force the blockchain to synchronize this database. Thus, all information about our money, its amount, and its owners will be stored not on one computer of a particular person, but on all at once. In addition, since there are hundreds of thousands of them, it becomes much more difficult to lose this information.
A bitcoin block is just a block with data, a regular structure that stores some values. Most often, this is the height of the block (the block number in the blockchain itself), hash (the unique fingerprint of this block), the time when it was mined, by whom it was mined, and many other fields. This block stores general information and transactions. Transactions are used here precisely in the banking concept. This is the amount of money that came from one account to another account and from one person to another person. In addition, we can see the number of bitcoins that are processed in the block itself.
At the time of Bitcoin creation, people tried to avoid creating a large number of blocks. It was important that not all transactions were placed in a single block and there were no multiple blocks for a single transaction. It’s necessary for the blockchain base to be of an acceptable size.
Because of this problem, the Difficulty parameter appeared, which helped in creating new blocks. Its main task is to control the speed of creating new blocks and make sure that all 2016 blocks are created every 2 weeks (1 block per 10 minutes). How does this happen? A block is created, all transactions are placed in it, and the mining process begins. Only then, this block is sent to the blockchain. The main task is 10 minutes for the mining process and making it possible to create blocks in the network regardless of how many people are mining Bitcoin or how many users are in the network.
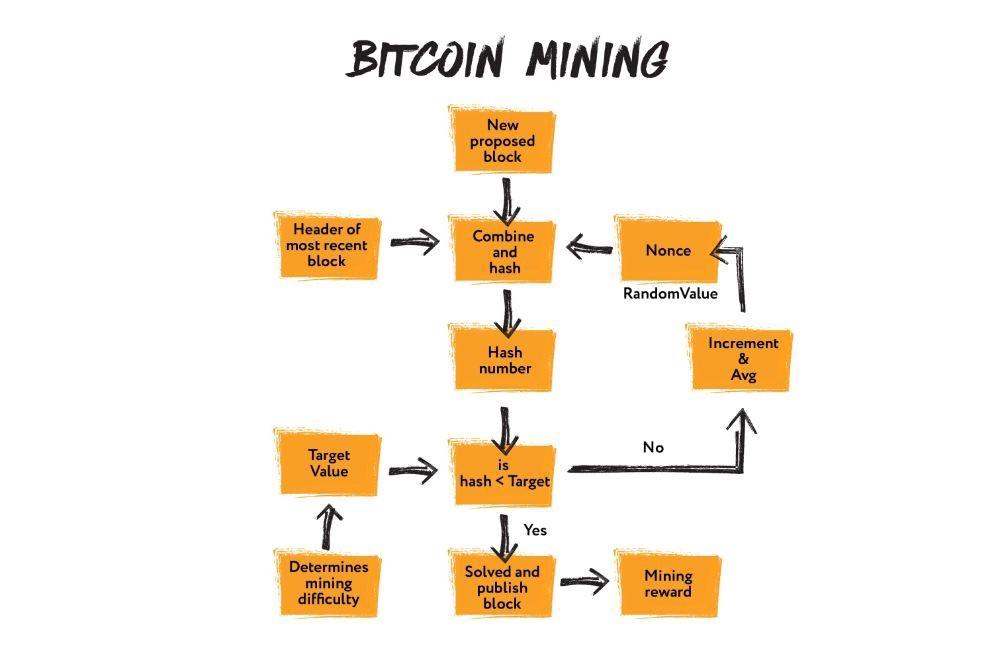
It is a rather simple process. We have a block (with its own hash value, time, etc.) and a number called NONCE.
NONCE is an abbreviation of Number used only once. The NONCE number is a regular counter from 0 to infinity. NONCE, together with the hash value of the previous block, is added to the block data, then its HASH is calculated. After that, certain conditions are checked. If the HASH is less than the target value, then the block is mined, which means the condition is satisfied and the block goes into the blockchain. If the HASH is greater than the target value, then NONCE is increased, is again added to the block and the header of the previous block again, the HASH is recalculated, verification is done, etc.
How can we compare HASH and target value, and what’s the point of this? HASH is a set of bits, and bits are a number. That is, HASH is a big number. When we add some kind of counter (NONCE) to HASH, then we change it. And when we check if the HASH is less than a certain number, we cut off a sufficiently large number of HASHes that are not valid.
In fact, it is only necessary to simply make the computer work and to make the process of the block creating not so easy. If this process were simpler, each person would be able to create a block. This can lead to problems with double-spending.
Thanks to the speed of computers, without this verification, it would be possible for one person to transfer funds to another and then rewrite the entire history as if they had not transferred anything.
Today it is possible only through mining or currency exchange.
A cryptocurrency exchange is a community of people who are interested in buying and selling cryptocurrency. If a person wants to buy bitcoin, then they will find the one who will sell it at the exchange. Such exchanges exist in order to exchange bitcoins for dollars, euros, etc., i.e for ordinary fiat money.
If one day people decide that milk in the store can be bought with bitcoins, the need for banks will disappear, as they will not be needed. It is not happening, because people value dollars, euros and other currencies more than bitcoin because money can be felt.
If you look at the development trend of money, we will see that now there are more and more disposals of digital assets. One of them is Ripple. Currently, banks use this technology to conduct transactions between themselves. Ripple extends the abstraction of consistent storage and uses Distributed Ledger Technology.
In addition to Bitcoin, there is another crypto technology Ethereum, and its cryptocurrency is Ether. However, this system has a significant difference. Until recently, Bitcoin’s main and only sphere of application has been money, namely, saving transactions and transferring funds from one person to another. Ethereum has other features. It opens up new perspectives for us and is not limited to transferring money. There is the possibility of transferring houses, cars, and other things. It becomes possible to abstract from the transfer and to proceed to a simple commission of some actions (as before, for example, payment). That is, we replace money and its transfer with information and some actions on it.
How can we describe this information and the actions taken with its help? There are programming languages allowing us to do it. Using programming languages we can describe what we are doing, how we are doing it, with what conditions, etc. Ethereum is not about money, but about smart contracts. Simply said, this is a platform for creating smart contracts.
A smart contract, in the first place, is simply an algorithm that runs on the blockchain. This algorithm is performed by all people who have an Ethereum node. These smart contracts are carried out by those who hold the blockchain database and are engaged in mining.
Let’s look at how a smart contract work on a simple example of buying a house. So, we have a buyer and a seller. In order to sell this house, they must contact a bank, a special organization, a lawyer or other third parties. These third parties receive some part of the transaction amount upon sale. Third parties are needed to confirm that the buyer has transferred the money, and the seller transferred the rights to the house. But you can replace the third party by code. In this situation, we state that the code is equal to law. The usual contract that is concluded during the transaction, we can translate into a programming language. If the buyer transferred money to the smart contract, the contract records the transfer of money and automatically transfers the rights to the house to the buyer. And the money received as a result of this transaction, the contract transfers to the seller. No third party is needed here that will confirm all this. Most importantly, the result execution of this smart contract is recorded in the blockchain.
Smart contracts are written with special programming language Solidity. We write a contract and then compile it with the Ethereum compiler. It creates a bytecode for EVM. Essentially, all of Ethereum with the blockchain is spinning in the Ethereum Virtual Machine. This is the same virtual machine as, for example, GraalVM or JVM for Java, etc. Blocks are stored in it, and EVM bytecode is written to a block. What is written into this block is the Deployed contract. After that, we can access it, call it, since we know it is stored in this block.

But even in the case of a smart contract, there are certain things that need to be considered. Suppose we have a contract that we can create and ask someone to perform it. Accordingly, the contract will not be performed with us. But why not then create an endless cycle that will run forever and the contract will never be fulfilled? A certain condition is needed that does not allow this to be done. We need gas to launch a smart contract.
So how do we can ask someone to fulfill a smart contract? To do this, you need to create a transaction and transfer a certain amount of Ethereum, which is converted to gas. Each operation performed in bytecode will cost a certain amount of gas. The contract will stop running when the gas runs out. And if we want to fulfill the contract, then we need to give more gas.
IPO is pretty a standard thing that has been around for many years. Let’s imagine that we have a sufficiently developed company and we need a large amount of money for further development. What can we do in such a situation? We can contact the investor and ask him for money. But one investor will not have that much money. It becomes clear that we need to attract resources somehow. So the company contacts banks and offers the exchange and the entire community purchase of shares.
IPO or initial public offering is a public offer of company shares for sale. When the investors and organizations purchase the shares, all the money received is transferred to the company’s account. After receiving the money, the company can invest it in further development.
With cryptocurrencies coming into the picture, such a concept as ICO (initial coin offering) appeared. Here already offer not shares, but coins. And we can describe the transfer of this new money with the help of smart contracts that Ethereum allows us to create. In Ethereum itself, we can create tokens.
A token is a unit of value and a unit of account most commonly used inICO. This is an internal asset of the project, a kind of analog of the company’s shares. There is an ERC20 standard that defines a set of rules that must be followed in order for a token to be accepted and be able to interact with other tokens on the network. Anyone can create tokens now. On average, $100 will be enough to launch this smart contract in the blockchain. Thus, anyone at home with a laptop is able to implement the ERC20 standard and create their own token in the Ethereum database.
How is this related to ICO? If we want to attract funds to our company, we can create a token. This requires minimal investment, which is not the case with banks. A Bank will not pay attention to small and medium-sized business, as they are used to working only with large companies. Everything is much easier with coins. After creating coins, we can run ads for the target audience so that people could buy these coins. After that, we will receive funds in Ether, which we will be able to withdraw and receive fiat money through crypto exchanges. If the price of the company increases, the price of tokens will also increase.
Ethereum used to be almost no different from Bitcoin. However, soon it is planned to replace the Proof of Work system with the Proof of Stake system. This will solve one of the most important problems, i.e. time of transaction creation. It used to take minutes. In addition, computing resources are needed, and a lot of funds are required to organize pools. These were the main reasons for switching to Proof Of Stake.
If Proof of Work requires a computer to perform many computational operations, for Proof of Stake it is enough to own a certain amount of cryptocurrency.
The more people enter the network, the more distributed the resources within the network become. Proof Of Stake allows miners to check more transactions when they have more Ether on their accounts. And if somebody has a large number of Ether on the account, then with a greater probability we can trust them, because they did not withdraw Ether and, on the whole, did nothing with them. Due to greater trust in them than in other network participants, we send them more transactions.
Another reason for Ethereum switch to Proof Of Stake is the speed. Using PoS you can significantly speed up the validation of the transaction. It is worth noting that, in addition to PoW and PoS there are many other different validation models.
At the moment, blockchain technology is one of the most promising developments in the world. With its help, you can revolutionize and automate a large number of activity areas.
In just a few years, blockchain has already gone from a novelty in the technological world to a tool that large banks, corporations, and governments are beginning to use, which only strengthens the belief that in the future this technology will reveal its potential even more.