The Future of Retail: Wearable Devices App Development for Ecommerce Success

This article explores how wearable apps redefine retail operations, supported by critical statistics and features. We delve into the advantages, challenges, development strategies, and cost analysis. Need a competitive edge? Consult with our experts now.
Reading time: 25 min.
Looking to boost your business profits? If you’re an e-commerce executive or store owner, you’re in luck. IntexSoft has rounded up everything you need to know about a game-changing tool: wearable apps. They’re trendy, they’re practical, and many retailers are already seeing actual results. It’s a solution you can trust.
What are wearable apps? These tools aim to redefine user experience, leveraging devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and AR glasses. They break from the mold of traditional mobile apps, prioritizing on-the-go interactions. For e-commerce businesses, wearable apps redefine how brands connect with customers and open doors for golden opportunities.
Now, about proving statistics.
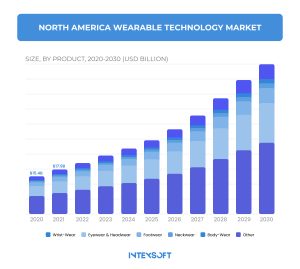
You can assess the dynamics in the image above. Although this data regards North America, the global situation is the same. In 2020, the wearable market was valued at almost $55 million. Fast forward to 2031, and that figure is expected to hit nearly $185 million, driven by a 14.6% annual growth rate that signals massive consumer adoption.
Wristwatches account for almost 43% of wearable device sales, cementing their position as the most ubiquitous choice in this booming industry.
One in four wearable tech users prioritizes convenience. These customers value seamless access to instant notifications, voice-activated assistants, and mobile payments. This is why many see wristwatches as a practical gateway for e-commerce purchases.
While purchasing directly from wearable devices remains uncommon today, it is only a matter of time before this technology becomes a routine part of commerce. Forward-thinking companies have an opportunity to leverage wearables now, not only as tools to enhance customer understanding but also to strengthen brand recognition and loyalty. Waiting too long to adapt could mean falling behind in a rapidly evolving market.
We should also emphasize that e-commerce purchases are significantly influenced by current trends, particularly AI. In the world of wearables, AI has emerged as a force, captivating industry leaders and reshaping consumer experiences. Forecasts indicate that by 2026, four out of ten wearable devices will operate with advanced AI functionalities.

At first glance, wearable apps might look like mobile apps, but they offer different functionalities. Check out the table below for a closer look at the key differences.
| Aspect | Wearable Apps | Mobile Applications |
| Device Compatibility | Depends on the compact nature of wearable devices. These devices are purpose-built for specialized, real-time functionality. | Designed for smartphones and tablets, benefiting from larger screens, more powerful processors, and broader functionality. |
| User Interaction | Interaction in wearable apps is designed for quick, efficient access, with fewer user inputs required. These devices utilize gestures, voice commands, and haptic feedback, emphasizing simplicity over complexity. | Mobile applications engage users more extensively, offering a range of input methods such as touchscreens, keyboards, and even physical buttons. |
| Interface Design | Wearable app design is defined by its minimalist approach—small screens necessitate highly focused, immediate communication, often stripping away non-essential features. | By virtue of their larger displays, these applications can afford richer, more detailed interfaces, designed for extended use and multitasking. |
| Functionality Scope | The functionality is deliberately narrow, catering to specialized tasks like health tracking, notifications, and brief interactions. This limits their scope but maximizes their efficiency for targeted uses. | More versatile, handling complex and diverse functions. They support multitasking, gaming, social networking, and e-commerce—tasks that demand the power of larger hardware and more memory. |
| Hardware Dependence | Сlosely intertwined with the specific hardware of wearable devices. Sensors, GPS, and heart rate monitors are critical, shaping how the app delivers data and interacts with the user. | While they also utilize hardware features such as cameras and microphones, their design is not as deeply embedded in the device’s physical capabilities. They rely more on software optimization to harness device power. |
| Battery Constraints | Wearable devices often face tighter battery constraints, a result of their compact design. As such, wearable apps are engineered for power efficiency, ensuring that devices remain operational for extended periods without frequent recharging. | Can afford to be more power-hungry, as mobile devices come with larger batteries. They often intended to support long, continuous usage, including gaming or heavy app multitasking. |
| Background Apps | Generally focus on one core function at a time. They are designed for brevity—quick bursts of utility, with limited or no background activity to conserve energy and processing power. | Often run numerous tasks in the background—whether syncing data, handling notifications, or maintaining active connections. |
| Cross-Platform Support | Inherently tied to the ecosystem of the wearable device they run on. They rely on device-specific APIs, making them largely non-cross-platform and more closely aligned with the brand’s ecosystem. | Tend to be more adaptable, often built to work across multiple operating systems, such as iOS, Android, or cross-platform frameworks, which allows them to reach broader markets. |
| Personalization | Provide hyper-personalized experiences, drawing from real-time data like step count, heart rate, and location to tailor notifications and suggestions. | Also personalize the user experience, but the scope is typically broader, drawing on historical user data, preferences, and inputs to create a more generalized experience. |
| Connectivity | Rely on intermittent connectivity, often syncing via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to smartphones or cloud services. This allows them to offer streamlined services without the need for constant data access. | More robust connectivity, operating independently or tapping into cellular data and Wi-Fi to provide continuous access to cloud-based features and services. |
| Purpose | Optimized for quick, on-the-go utility, designed to enhance daily tasks like checking notifications or tracking workouts, with a focus on simplicity. | Offer more comprehensive experiences, suited for long-term, involved use—enabling users to work, socialize, shop, and entertain themselves across numerous platforms. |
| Market Adoption | Remain in a phase of growth, still carving their place in niches such as fitness, healthcare, and personal convenience. The market is poised for expansion, driven by rising consumer interest in health tracking and instant access. | Firmly established, deeply embedded in modern life. From e-commerce to entertainment, they are ubiquitous, offering unparalleled accessibility and integration with countless services. |
| Feature | Why It Matters | Real-World Impact | Additional Insights |
| User-Centric Design | A wearable app must prioritize simplicity and intuitive navigation to fit the compact screens of wearables. | When users encounter simple, intuitive design, they are more likely to stay engaged, navigating the shopping journey with ease. | Clear typography and menus remove distractions, allowing users to focus on what matters most. Optimizing for smaller screens is about eliminating unnecessary clutter. |
| Integration with Mobile Apps | Wearable apps shouldn’t stand alone—seamless syncing with mobile apps enhances functionality and user experience. | Users can start browsing on their smartwatch and complete purchases on their smartphone. | Integration allows for cross-platform continuity, enabling users to continue their shopping journey uninterrupted between devices, enhancing user retention. |
| Real-Time Notifications and Alerts | Instant updates on promotions, order status, or low-stock items keeps users engaged and informed. | Notifications prompt immediate responses, boosting sales and enhancing customer happiness. | Push notifications should be timely, relevant, and personalized. Effective alerts also reduce the risk of cart abandonment by informing users of flash sales or limited-time offers. |
| Personalization and Recommendations | Customizing user experiences through tailored product suggestions and browsing history increases relevance. | Shoppers feel valued and are more likely to make purchases aligned with their preferences. | With the help of AI and machine learning, wearable apps can track previous behaviors and suggest products, enhancing the shopping experience with a personal touch. |
| Payment Solutions | Simplified payment processes, such as tap-to-pay or one-click options, ensure quick, hassle-free checkouts. | Fast payment options reduce cart abandonment rates and boost overall transaction speed. | Integrating mobile wallets (like Apple Pay, Google Pay) or one-click payments on wearables makes transactions easier and faster, meeting the on-the-go needs of users. |
For C-level executives evaluating the decision to outsource wearable app development, the big question is: What does it really cost, and what factors influence that price tag?
What do you want the app to do? Basic apps that send push notifications or track simple metrics are less expensive. Every added feature increases development hours. Complex apps that integrate with AI offer personalized recommendations, or syncing with multiple platforms costs more.
Choosing the operating system for your app can significantly affect the budget. Developing for a single platform, like Wear OS or watchOS, is more straightforward than creating a cross-platform solution. However, limiting yourself to one platform might restrict your audience. Cross-platform development often comes with higher upfront costs but may deliver a better return on investment by reaching more users.
Intuitive, visually appealing designs are what wearables demand. However, this task is impossible without team members with specialized expertise in creating a user interface tailored to a small screen and a smooth user experience. The important point to remember is that cutting corners on design might save costs initially, but in the long term, such an approach has its consequences. For example, poor adoption rates and lost revenue.
The app you see on a wearable device is only half the story. A robust backend system is essential for storing and processing data, integrating with e-commerce platforms, and ensuring real-time functionality. The more data your app handles and the faster it needs to process it, the higher the investment in backend development.
Seamless integration with existing e-commerce platforms is a must. This includes syncing product catalogs, enabling secure transactions, and incorporating marketing tools like personalized discounts. Custom integrations, while necessary, often require significant development resources, especially when working with legacy systems.
Security isn’t optional, especially when dealing with sensitive customer data. Implementing robust security measures—such as encryption, secure authentication, and GDPR compliance—requires expertise and additional development time.
By focusing on wearable apps, e-commerce businesses can better equip themselves to conquer the world of sales. Here are the benefits online store owners can leverage confidently:
Wearable devices, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, open a big window to the future that has already come. The shopping journey has changed. The principles of online stores interacting with e-commerce brands have also changed drastically.
Today, we have direct communication channels to send personalized notifications—such as exclusive deals or new arrivals—to a customer’s wrist.
You may look at the study by Retail TouchPoints that highlights how timely and relevant messages delivered through wearables impact customer loyalty. They boost it and foster a sense of personal connection. Such direct engagement always leads to higher conversion rates.
Imagine a commuter ordering a product with a simple voice command to their smartwatch. This represents maximum convenience. Customers don’t need to pull out a smartphone or log into a computer; making a purchase becomes an option accessible everywhere with minimal effort, often in under a minute.
This ease of access reduces friction and can potentially boost sales, especially among young, active generations who are keen on new technologies and truly value time-saving solutions.
Retailers find this benefit worthwhile. The core lies in the fact that wearable devices offer a direct connection to consumers. Advanced sensors capture individual metrics such as physical activity levels and location data, providing businesses with accurate and actionable insights.
Why is understanding when and where customers are most active crucial for marketers? Crafting targeted strategies with the information above takes marketing to the next level. The chances that promotions will reach consumers at the optimal time and place are rising. Marketers gain essential tools to influence purchases.
The last benefit is closely connected with the brand’s long-term growth. The crowded market dictates its own laws for e-commerce. To set apart competitors, you should adopt wearable technology as soon as possible. These innovations signal that your company is forward-thinking.
Tech-savvy consumers gravitate toward innovators. As an early adopter, you gain the opportunity to act, potentially opening the door to a larger market share.
If you need additional proof of the above fact, consider the following statistics: The rise of wearable gadgets has led to a 15% increase in retail sales for electronic devices. As we highlighted at the very beginning of the article, consumer interest in this technology will grow in quantum leaps.
Stepping into wearable app development? It’s not without its challenges. From technical difficulties to user experience concerns, companies have a lot to consider. But with a seasoned team, these hurdles are manageable. Let’s dive into the major challenges and their solutions.
Creating a wearable app isn’t as simple as shrinking a mobile app. This common mistake often spells trouble for developers. Instead, reimagine how users engage with wearable devices.
Here are some practical tips to guide you.
Define your app’s purpose and its audience. What problem does it solve? Research competitors to identify your edge. Select the platform—Wear OS, watchOS, or Tizen—and account for its unique constraints.
Each operating system carries its quirks. Whether it’s Google’s Wear OS or Apple’s watchOS, choose a platform that matches your audience and app functionality. If you aim for cross-platform reach, plan for complexity.
Wearables demand streamlined interfaces. Forget flashy clutter. Prioritize what users need most, accessible at a glance. Utilize touch, voice commands, and sensor integration to create intuitive interactions.
A wearable’s limited battery doesn’t allow for inefficiencies. Minimize notifications, streamline processes, and use lightweight code. An energy-efficient app keeps users engaged.
Wearables collect sensitive data—heart rates, GPS locations, more. Encrypt everything, and adhere to laws like GDPR or HIPAA. Transparency in data handling builds trust.
A wearable app’s power lies in its ecosystem. Ensure flawless integration with phones, tablets, and IoT devices. Real-time syncing creates a frictionless experience.
Perfect code doesn’t guarantee success. Test your app under real-world conditions—on hardware, with sensors, across environments. Early prototypes can catch critical flaws.
Deployment is the beginning. Release updates, monitor feedback, and adjust to user needs. Adaptability ensures longevity.
Technology races forward—AI, AR, and 5G are reshaping wearables. Build with future scalability in mind to seize tomorrow’s opportunities.
By the close of this year, one in four wearable devices is anticipated to meet eco-friendly and sustainable standards. This is the factor many users appreciate greatly. However, to achieve benefits with wearable apps, they need to be well-crafted.
Outsourcing can be the most efficient way to build a wearable app for e-commerce, but selecting the right development partner is critical. When evaluating potential teams, consider those that excel in:
Costs can start at $30,000 for a basic app and soar past $300,000 if you’re crafting a powerhouse of features. Every decision, from platform selection to security features, impacts the final bill.
For C-level executives, investing in wearable app development isn’t just about cost—it’s about choosing a partner who understands your vision and can turn it into a tool that enhances customer experience and drives revenue. The right app can transform your e-commerce strategy, but it starts with understanding the factors that shape the price.
IntexSoft is always seeking the most beneficial options for our clients. We focus on the overall development cost rather than solely on hourly rates. Our experts assess technological capabilities and approaches to AI integration, ensuring these are reflected in the overall project cost savings.
Want to collaborate with a leading wearable app development company? Contact us today.